- DCCN HPC Guide
- Introduction
- 1. Linux Basic
- 2. Bash scripting
- 3. Using the HPC Cluster
Getting access to the HPC cluster
Obtain an user account
You should receive a pair of username/password after following the DCCN's check-in procedure. If you do not have a account, ask the TG helpdesk.
Note: The user account here is NOT the account (e.g. u-number) given by the Radboud University.
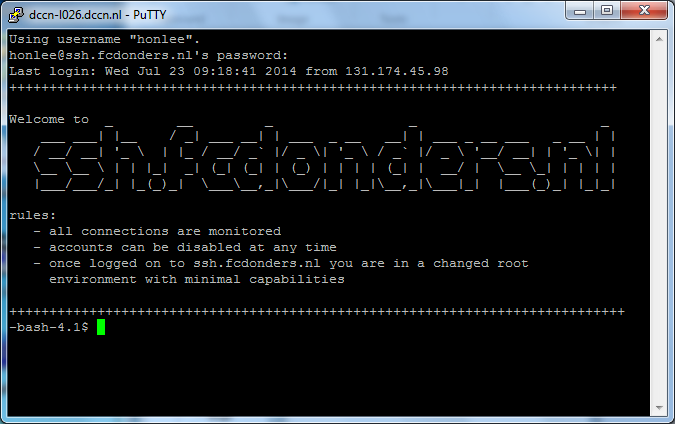
SSH login with Putty
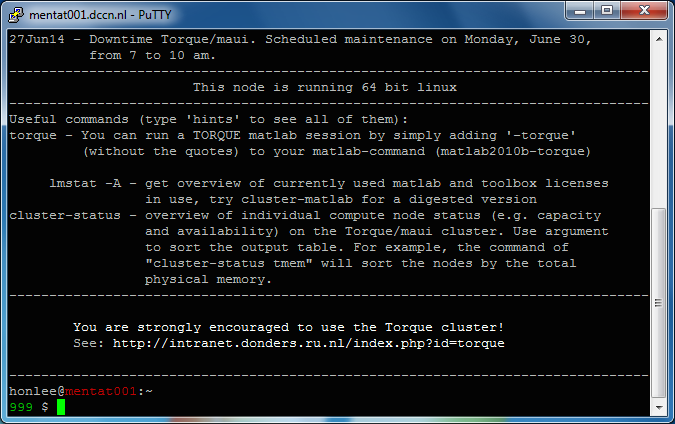
Follow the steps below to connect to one of the cluster's access nodes, using the SSH.
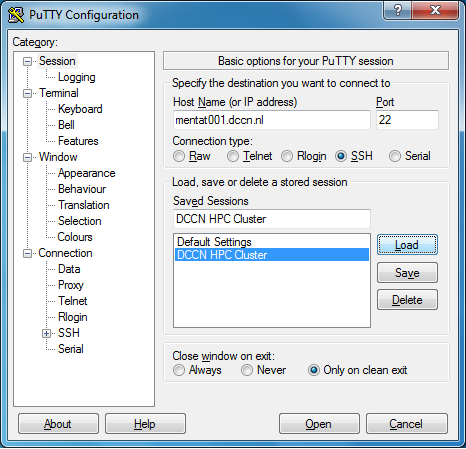
- Start putty on the Windows desktop
- Configure putty for connecting to, e.g.,
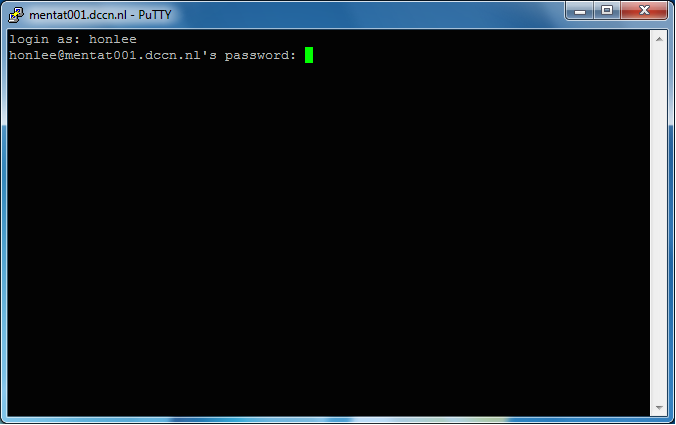
mentat001.dccn.nl - Login with your username and password
- Get a test-based virtual terminal with a shell prompt
Screenshots of the four steps are shown below:

SSH logout
You can logout the system by either closing the Putty window or typing the command exit in the virtual terminal.
VNC for graphic desktop
For the first-time user, type
$ vncpasswdin the putty terminal to protect your VNC server from anonymous access before following the instructions below.
Firstly, start the VNC server by typing the following command in the putty terminal:
$ vncmanager
Follow the step-by-step instructions on the screen to initiate a VNC server. See the screenshots below as an example.
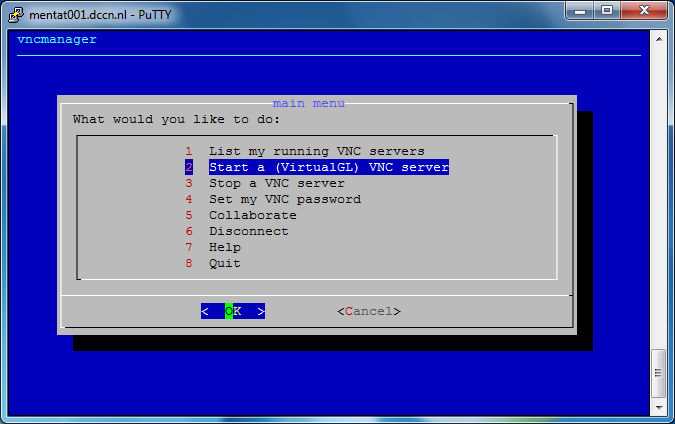
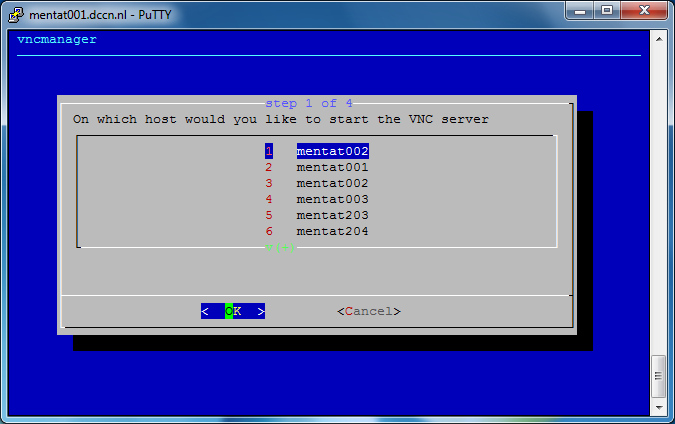

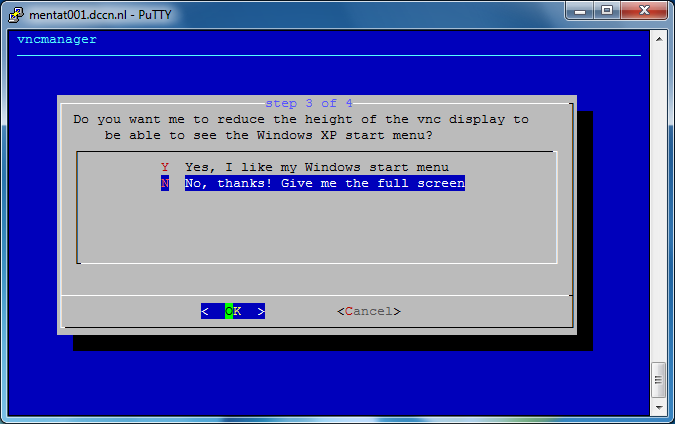
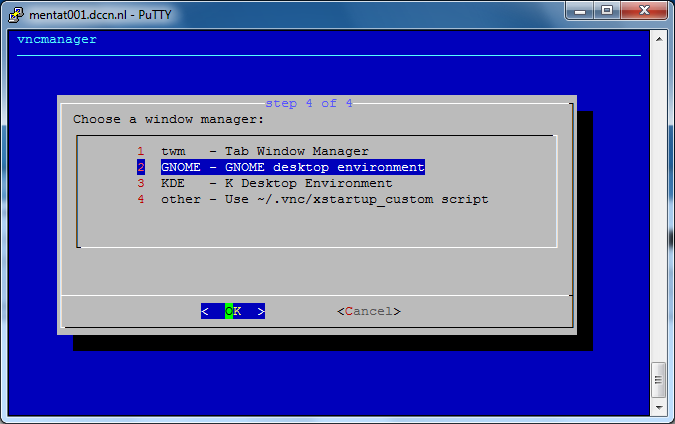
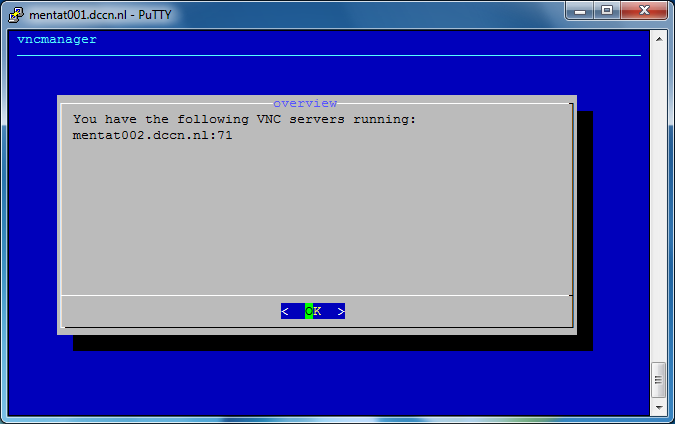
In the screenshots above, we have started a VNC server associated with a display endpoint mentat002.dccn.nl:71. To connect to it, we use a VNC client called TurboVNC. Follow the steps below to make the connection:
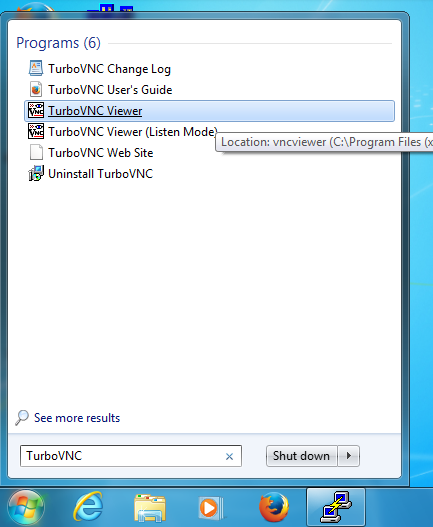
- Open TurboVNC application
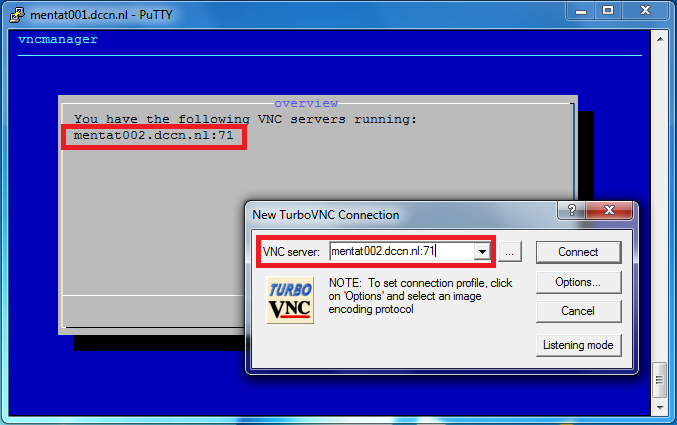
- Enter the display endpoint (
mentat002.dccn.nl:71) as the VNC server - Enter the authentication password you set via the
vncpasswdcommand - Get the graphical desktop of the access node
Screenshots of those steps are given below:

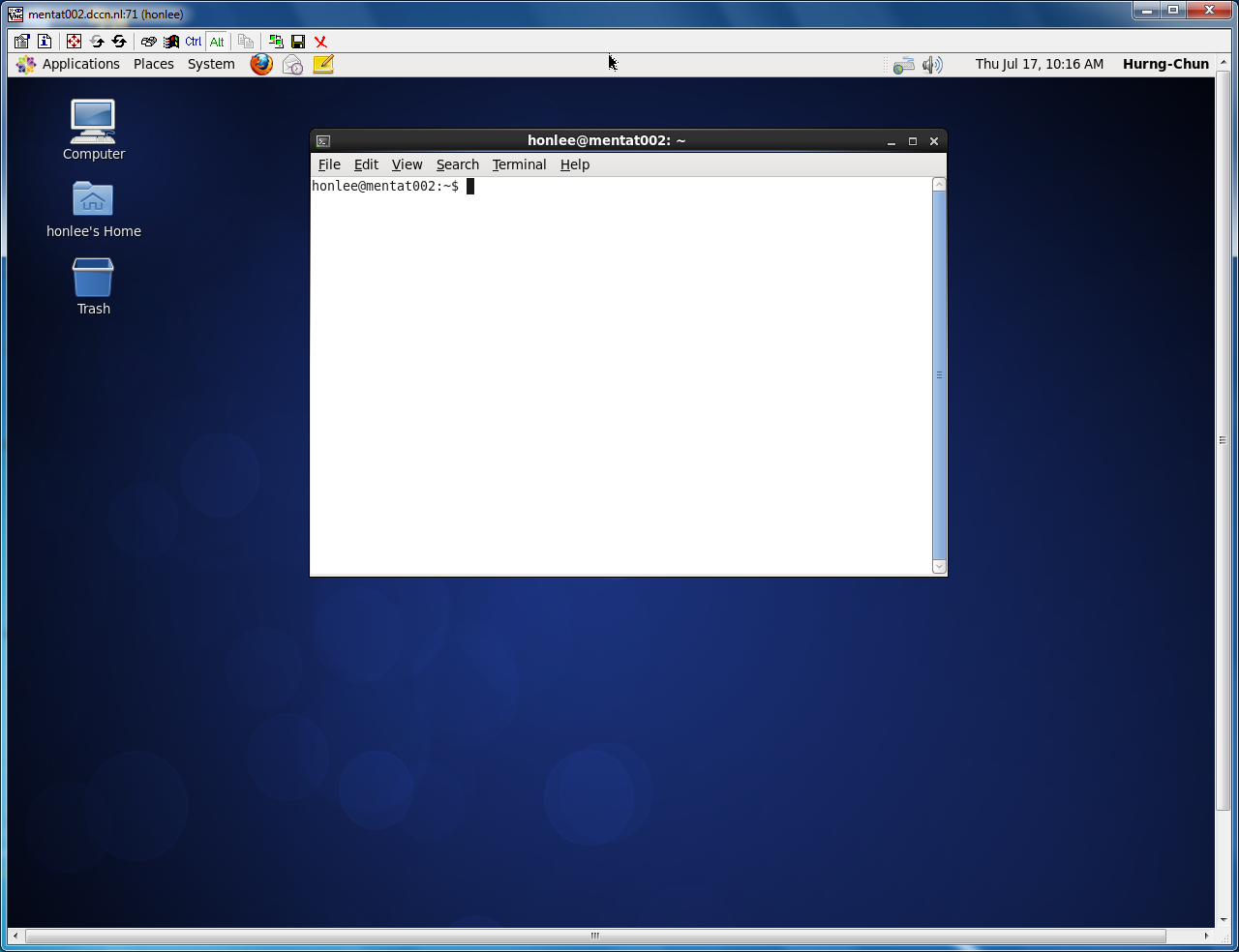
Disconnect VNC server
To disconnect the VNC server, simply close the TurboVNC window in which the graphical desktop is displayed. The VNC server will remain available, and can be reused (re-connected) when you need to use the graphical desktop again in the future.
Warning: DO NOT logout the graphical desktop as it causes the VNC server become unaccessible afterwards.
Terminate VNC server
Since the graphical windows manager takes significant amount of resources from the system, it is strongly recommended to terminate the VNC server if you are not actively using it. Terminating a VNC server can be done via the vncmanager command. The steps are shown in the screenshots below:
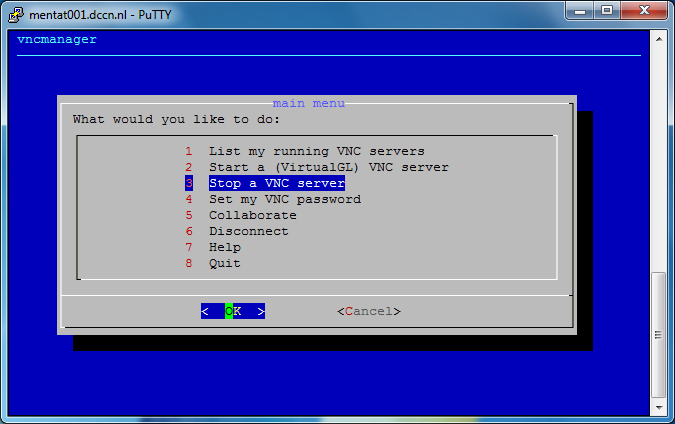
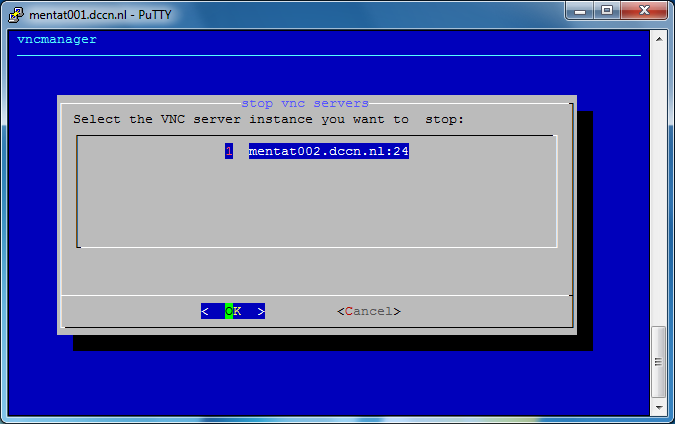
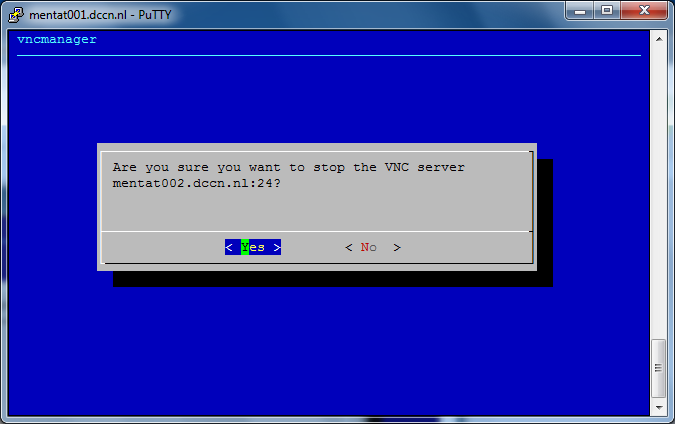
Not in the DCCN network
If you are at home or on travel, or connecting your personal laptop to the edurom network, you are not allowed to connect to the access nodes directly as they are in the DCCN network protected by a firewall. In this case, you need to make the connection indirectly via the so-called SSH tunnel.
The SSH tunnel
A SSH gateway named ssh.fcdonders.nl is provided for setting the SSH tunnels. When setting up a tunnel for connecting to a target service behind the firewall, one needs to choose a local network port that is still free for use on your desktop/laptop (i.e. the Source port) and provides the network endpoint (i.e. the Destination) referring to the target service.
Tip: This technique can also be applied for accessing different services protected by the DCCN firewall.
Putty login via SSH tunnel
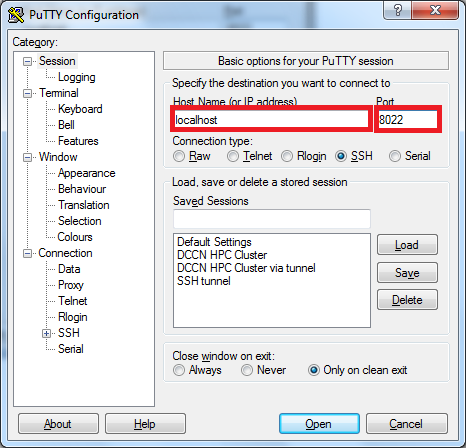
In this example, we choose Source port to be 8022. The Destination referring to the SSH server on mentat001 should be mentat001:22.
Follow the steps below to establish the tunnel for SSH connection:
- Start putty on the Windows desktop
- Configure putty for connecting to the SSH gateway
ssh.fcdonders.nl - Configure putty to initiate a local port
8022for forwarding connections tomentat001:22 - Login the gateway with your username and password to establish the tunnel



Keep the login window open and make another SSH connection to the local port as follows:
- Start putty on the Windows desktop
- Configure putty for connecting to
localhoston port8022 - Login with your username and password
- Get a test-based virtual terminal with a shell prompt



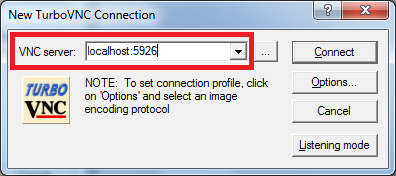
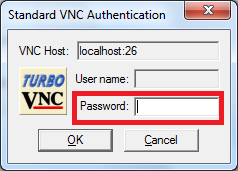
VNC via SSH tunnel
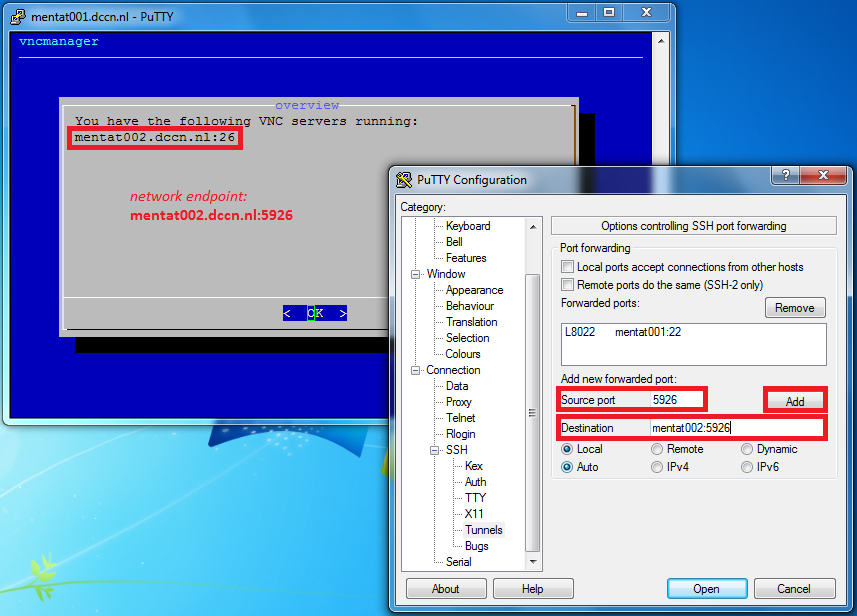
In this example, we choose Source port to be 5926. We also assume that a VNC server has been started on mentat002 with the display number 26. The Destination referring to the VNC server should be mentat002:5926.
Note: the network port number is always the display number plus 5900.
Follow the steps below to establish the tunnel for VNC connection:
- Start putty on the Windows desktop
- Configure putty for connecting to the SSH gateway
ssh.fcdonders.nl - Configure putty to initiate a local port
5926for forwarding connections tomentat002:5926 - Login the gateway with your username and password to establish the tunnel



Keep the login window open and make VNC client connection to the local port as follows:
- Open TurboVNC application
- Enter the display endpoint (
localhost:5926) as the VNC server - Enter the authentication password you set via the
vncpasswdcommand - Get the graphical desktop of the access node